CASTOR (Code Aérodynamique pour la Simulation de Turbines OffshoRe) is a GPU-based free vortex wake software for the simulation of wind turbines aerodynamics. It contains several features:
- Wake representation with filament and/or particles
- Advanced wake accommodation: shed-merging, trail-merging, tip-vortex concatenation
- Coupled with hydro-servo-aero-elastic solver DeepLinesTM
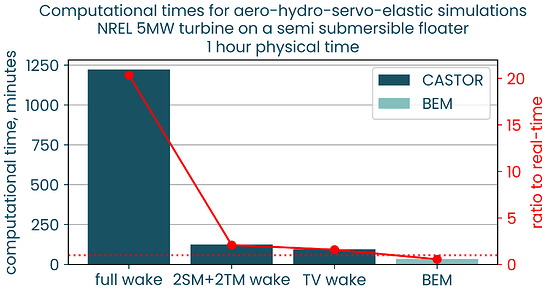
Advanced vortex accommodation techniques are capable to reduce the calculation time to almost real-time response, close to BEM:
Illustration of the wake accommodation techniques with the Mexico turbine
-
full wake
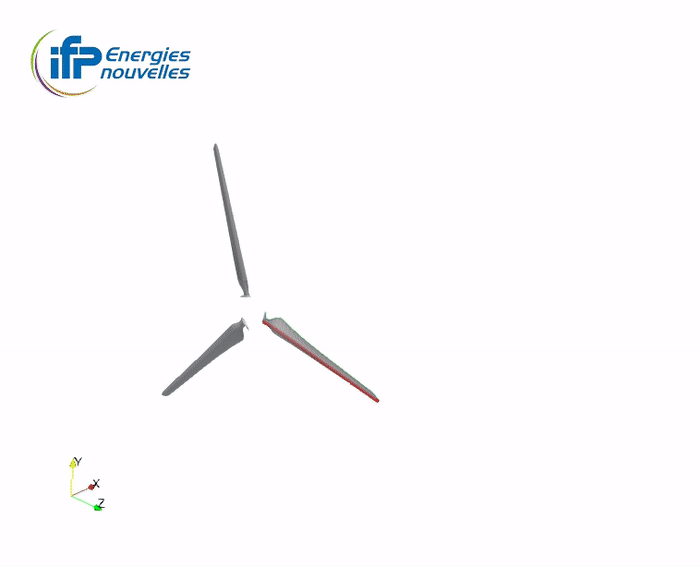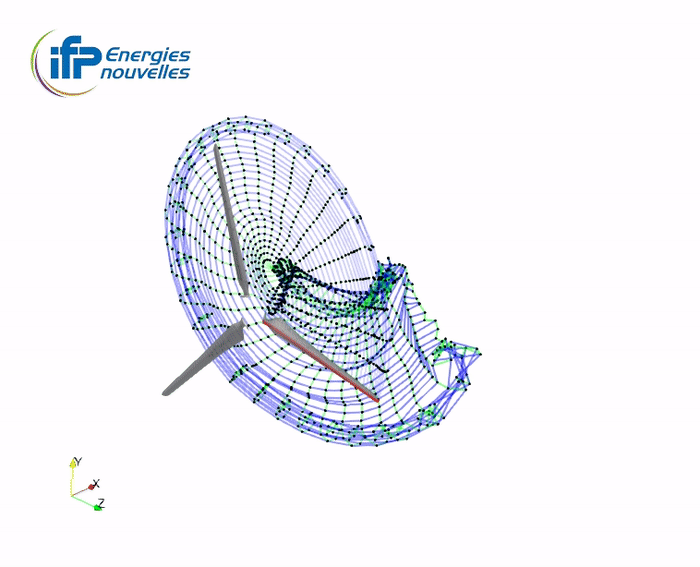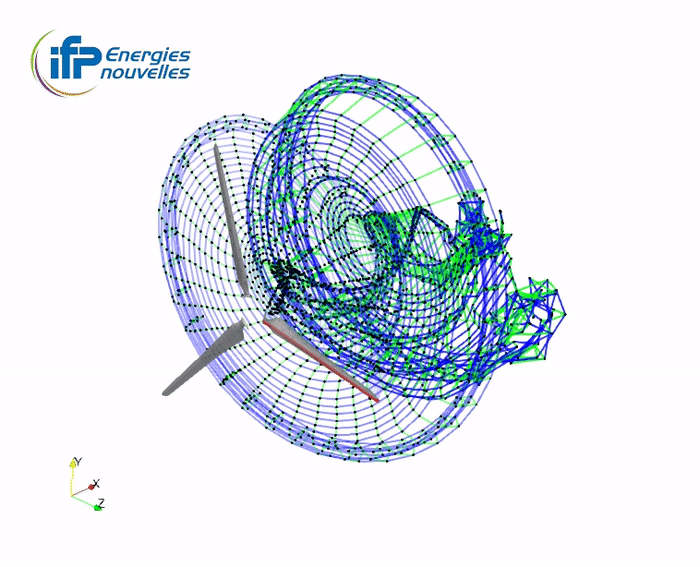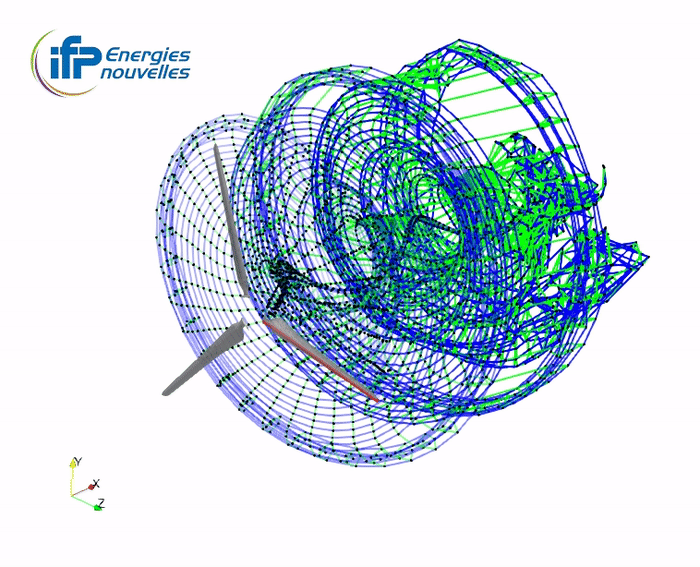
-
2SM+2TM wake (2 shed-merging + 2 trail-merging steps)
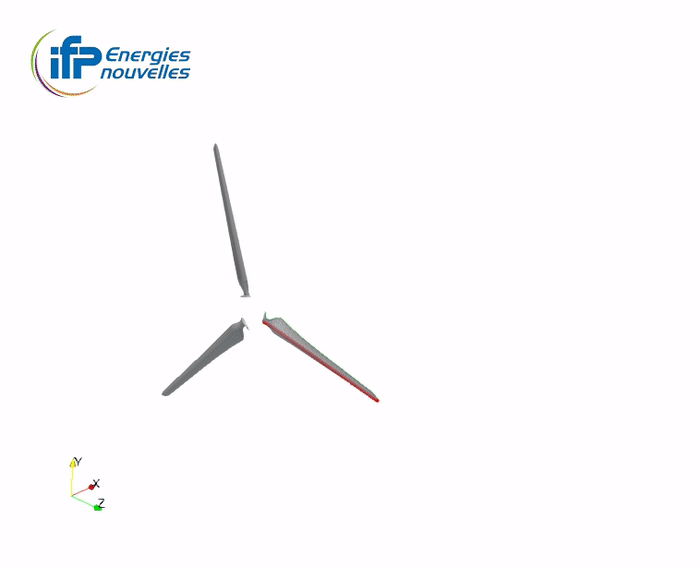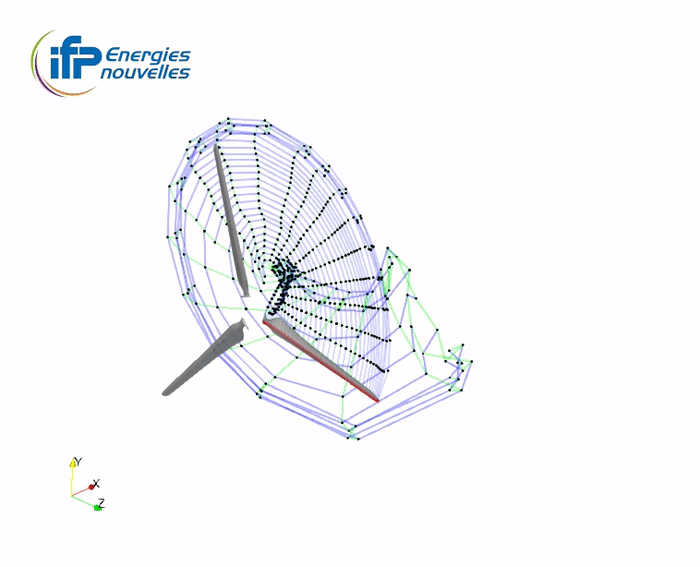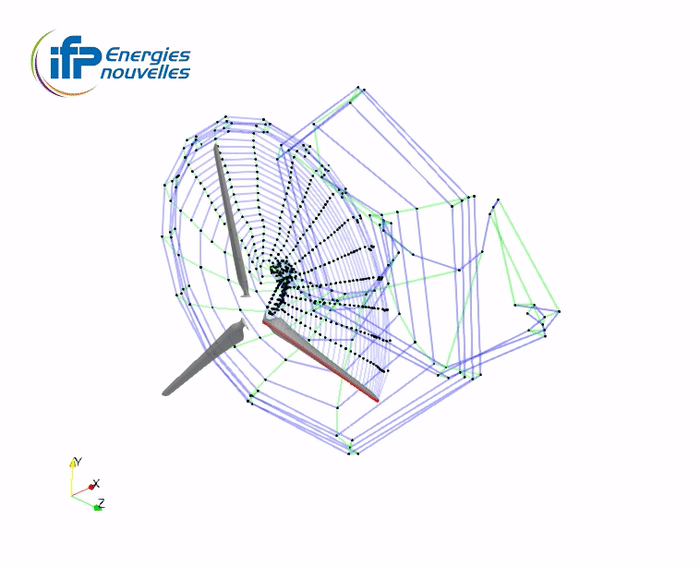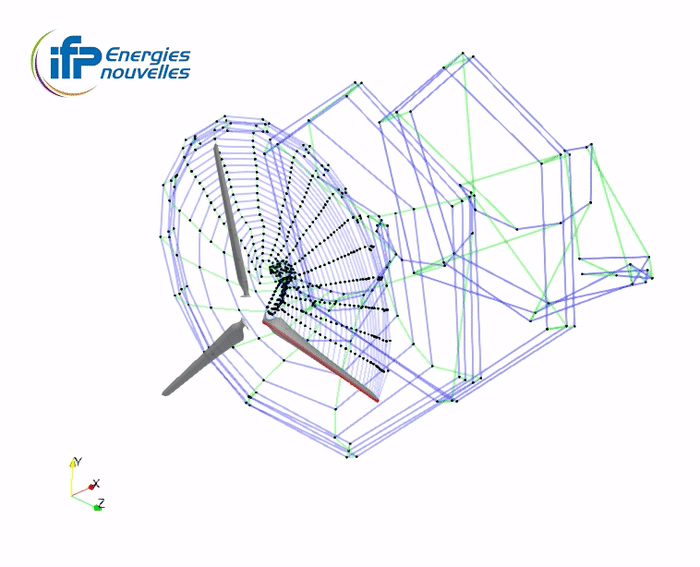
-
TV wake (tip-vortex concatenation)

To know more:
- Blondel et al 2016 Validation and comparison of aerodynamic modelling approaches for wind turbines, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 753, 022029, 10.1088/1742-6596/753/2/022029
- Blondel et al 2024 Towards vortex-based wind turbine design using GPUs and wake accommodation, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2767, 052016, 10.1088/1742-6596/2767/5/052016
- Le Guern et al 2024 Partitioned time couplings of an aero-mechanical wind turbine problem, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2767, 022012, 10.1088/1742-6596/2767/2/022012
Participation in International Energy Agency (IEA) Wind tasks:
-
Task 29: Boorsma et al 2023 Progress in the validation of rotor aerodynamic codes using field data, Wind Energ. Sci., 8, 211–230, 10.5194/wes-8-211-2023
-
Task 47: Boorsma et al 2024 Challenges in Rotor Aerodynamic Modeling for Non-Uniform Inflow Conditions, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2767, 022006, 10.1088/1742-6596/2767/2/022006